You could build the best product out there seriously, world-class. But if your name doesn’t make people feel something or worse, if they can’t even recall it—what’s the point?
That’s where brand marketing comes in.
At its core, brand marketing isn’t about color palettes or catchy slogans. It’s about playing the long game earning trust, building emotional connections, and staying top-of-mind. It’s not just about selling a product; it’s about building meaning.
In a world where people scroll past dozens of brands before breakfast, only the ones that make people pause get remembered.
So, what is brand marketing?
Simply put, brand marketing is the strategy behind how a business shapes and communicates its identity. Every interaction packaging, ads, social posts, customer support, even hold music should quietly reinforce one message:
“This is who we are.”
Product marketing might say, “Buy now.”
Brand marketing leans in and says, “We get you. Stay a while.”
Let’s explore what brand marketing includes, why it matters, and how brands across industries use it to build loyalty and long-term value.
Key Components of Brand Marketing
Strong brands are built intentionally. Think of brand marketing like building a home solid foundation, thoughtful structure, and a vibe that keeps people coming back.
1. Brand Identity
This is your brand’s face and voice.
It includes:
- Logo
- Colors & typography
- Visual style
- Tone of voice
- Photography and design language
Example:
- Nike’s swoosh doesn’t just signal sports—it represents grit, perseverance, and momentum.
- In healthcare, Mayo Clinic’s calming colors and clean fonts communicate safety, trust, and expertise.
When emotions are high (like health decisions), visual reassurance matters.
2. Brand Story
People connect with stories—not products.
A strong brand story ties together:
- Why you started
- What you believe
- Where you’re going
Examples:
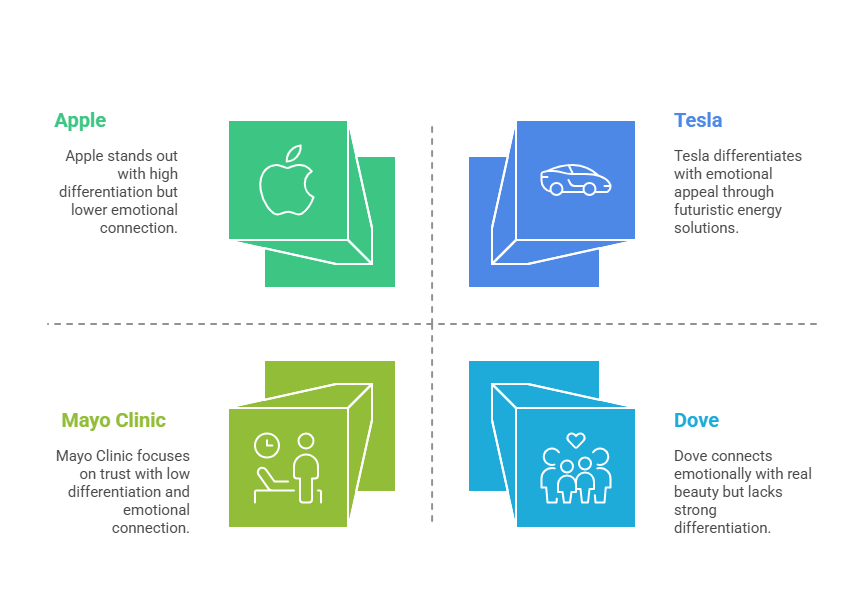
- Dove’s “Real Beauty” challenges conventional beauty standards.
- Patagonia positions itself as a climate activist—not just an apparel brand.
- Khan Academy promises that anyone, anywhere can learn.
These brands don’t just sell—they invite belief.
3. Brand Consistency
Consistency isn’t repetition—it’s recognition.
Your brand should feel like the same person everywhere:
- Website
- App
- Customer service
- Ads
- Social media
Apple nails this—from product packaging to keynote presentations.
In industries like finance, consistency builds trust. Whether a customer logs into an app or calls support, the experience should feel unified and reliable.
4. Differentiation
Why you?
Differentiation answers:
- Why should people remember you?
- Why should they choose you?
Examples:
- Tesla isn’t just selling cars—it’s rethinking energy and the future.
- charity: water uses transparency and storytelling to turn donors into participants, not just contributors.
Brand differentiation creates emotional preference before a purchase decision.
Objectives of Brand Marketing
Brand marketing goes beyond visibility. It’s about connection and meaning.
1. Build Brand Awareness
Not just recognition—but recall.
Example:
- Need a homestay? Most people instantly think Airbnb. That’s brand awareness done right.
2. Establish Brand Loyalty
When people see themselves in your brand, they stay—price fluctuations included.
Example:
- Starbucks transformed coffee into a lifestyle and a “third place” between home and work.
3. Stand Out in Crowded Markets
Features alone won’t save you in saturated spaces.
Example:
- Lemonade Insurance brought personality, simplicity, and tech into an otherwise dull category.
4. Encourage Advocacy & Word of Mouth
When brand marketing works, customers become fans.
Example:
- Glossier built its brand around community, not campaigns. The audience is the marketing engine.
Brand Marketing Strategies & Techniques
Brand building comes alive through consistent execution across channels.
Content Marketing
Education builds authority.
Examples:
- HubSpot uses free content to pull users into its ecosystem.
- Cleveland Clinic provides trustworthy health content, reinforcing medical credibility.
Social Media Storytelling
Social media is your brand’s personality on display.
Examples:
- Duolingo’s TikTok uses humor and chaos brilliantly.
- Nike highlights inspiration, causes, and athletes—never just products.
Influencer Partnerships
Alignment beats reach.
Example:
- Daniel Wellington scaled fast using micro-influencers, increasing sales by ~35%.
- Allbirds partners with sustainability-focused creators, keeping messaging authentic.
Paid Advertising
Paid ads amplify—but only when on-brand.
Examples:
- Coca-Cola leans on nostalgia and joy.
- Chime positions itself as the anti-traditional bank.
Different tones—same clarity.
CRM & Personalization
Personalization turns data into empathy.
Examples:
- Nordstrom remembers preferences.
- Coursera recommends relevant courses.
Relevance makes people feel seen—and valued.
Benefits of Effective Brand Marketing
1. Trust Converts Faster
Example:
- Amazon wins not just on selection, but on reliability and trust.
2. Higher Customer Retention
According to Bain & Company:
Increasing retention by just 5% can boost profits by up to 95%.
That’s the compounding power of brand loyalty.
3. Long-Term Relevance
Strong brands evolve without losing identity.
Examples:
- Netflix shifted from DVDs to streaming.
- LEGO revived itself through creativity and nostalgia.
In healthcare, Johns Hopkins built global trust through decades of consistent branding.
4. Premium Pricing Power
Example:
- Apple rarely discounts—yet demand remains high.
When brand identity aligns with customer identity, price becomes secondary.
Brand Marketing Examples That Work
Nike
“Just Do It” taps into self-belief and resilience. Every campaign reinforces that mindset.
Airbnb
They didn’t sell rooms—they sold belonging. “Live There” reframed travel.
Coca-Cola
Happiness, connection, celebration—decades later, the feeling hasn’t changed.
Mayo Clinic
In healthcare, brand equals trust. Mayo Clinic’s clarity and consistency reinforce authority.
Challenges in Brand Marketing
- Overcrowded Markets – Visibility isn’t enough anymore.
- Maintaining Consistency at Scale – Growth complicates alignment.
- Evolving Audiences – Gen Z values authenticity over polish.
- Measuring Intangibles – Translating sentiment into spreadsheets is tough.
Mistakes happen—but strong brands stay grounded in values.
Measuring Brand Marketing Success
Key Metrics
- Brand Awareness – Search volume, mentions, share of voice
- Customer Loyalty & LTV – Repeat purchases, memberships
- Brand Sentiment – Reviews, surveys, NPS, social listening
Tools
- Google Analytics
- HubSpot
- Brandwatch
- Hootsuite
According to Harvard Business Review, companies that track brand metrics effectively see up to 15% higher ROI.
Conclusion
Brand marketing isn’t about flashy logos or clever taglines.
It’s about showing u consistently until people don’t just recognize you, but trust you.
In an age of endless options and shrinking attention spans, the brands that win will feel human. Relatable. Real.
Because brands aren’t remembered for what they sell—but for how they make people feel.

