Marketing is constantly evolving. Every few years, new technologies reshape the way brands connect with their audiences. Today, one of the most transformative forces in this landscape is generative artificial intelligence. But what exactly is Generative AI in Marketing, and how does it apply to marketing? If you’re new to the concept, this comprehensive guide will walk you through everything you need to know — from the basics and practical use cases to ethical considerations and how to get started.
In this article, we will explore the foundations of generative AI, why it matters to marketers, and how businesses of all sizes can harness its potential. By the end, you’ll not only understand the technology but also be able to apply it to your own strategies with confidence.
Understanding the Basics: What Is Generative AI?
Generative AI refers to a class of artificial intelligence systems that can create new content. Unlike traditional AI models that simply analyze or classify existing data, generative AI creates new outputs — writing text, generating images, composing music, and even producing 3D designs. It works by learning patterns in large datasets and then using those patterns to generate new content that resembles the training data in structure, style, or substance.
At its core, it uses sophisticated machine learning models, often neural networks, trained on vast amounts of information. Once trained, these models can produce creative outputs that were not explicitly programmed. For marketers, this opens up exciting possibilities for automating and enhancing creative work.
How Generative AI Works
To truly appreciate the power of generative AI, it helps to understand its underlying mechanisms. At a high level, generative models operate through two main stages: learning and generation.
In the learning phase, the system ingests a large dataset — this could be text, images, or another type of content. Through a process known as training, the model identifies patterns, relationships, and structures within the data. For example, a text-based model may learn grammar rules, sentence flow, and stylistic nuances.
In the generation phase, the model uses what it has learned to produce new content. When given a prompt, it predicts what comes next based on the patterns it has internalized. The result is an output that reflects the characteristics of the training dataset but is not a copy of any specific example.
Some of the most well-known types of generative models include Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) and transformer-based models like GPT (Generative Pretrained Transformer). These systems have rapidly advanced over the past few years, enabling increasingly sophisticated and human-like outputs.
The Rise of Generative AI in Marketing
In recent times, generative AI has moved from a niche research topic to a central tool in the marketer’s toolkit. Businesses are recognizing that the ability to generate high-quality content at scale can significantly enhance productivity and creativity. It is especially valuable in environments where speed and personalization are critical.
At its essence, generative AI in marketing allows companies to produce tailored content, engage audiences in dynamic ways, and streamline workflows that once consumed vast amounts of time and resources. Companies both large and small are experimenting with these tools to improve their campaigns, refine messaging, and explore new creative possibilities.
Real-World Applications in Marketing
Generative AI is not a theoretical concept — it is already being applied across multiple marketing functions. Let’s explore some key use cases where this technology is making a tangible impact.
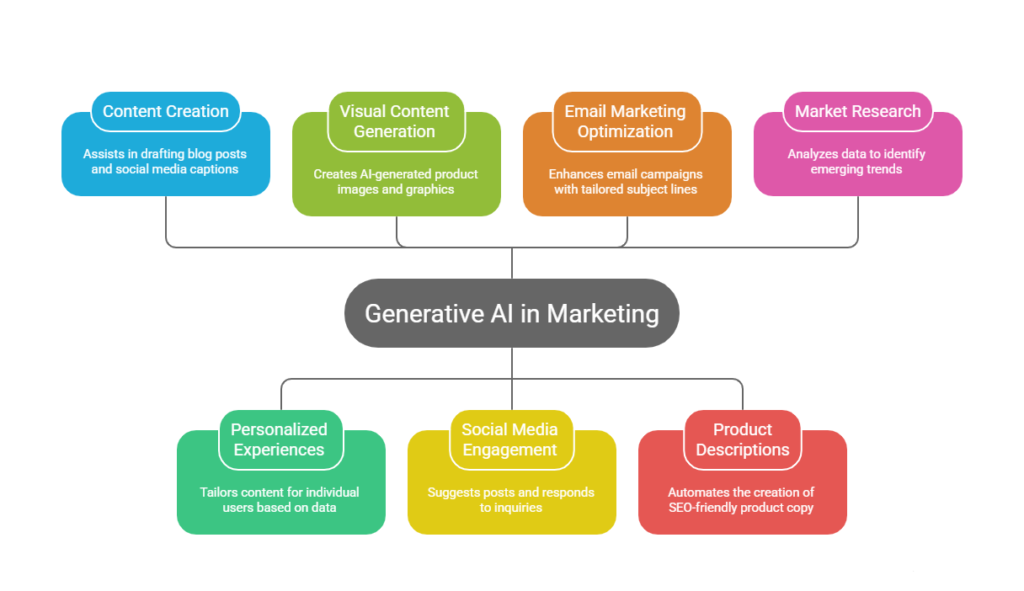
Content Creation and Copywriting
One of the most visible applications of generative AI is in the creation of written content. From drafting blog posts to generating social media captions, AI can assist marketers in producing compelling text quickly. Rather than replacing human creativity, these tools often serve as a starting point or a creative partner.
For example, a marketer might use an AI model to draft an article outline and first draft, then refine and personalize the copy to meet brand voice standards. This hybrid approach saves time while maintaining quality.
Personalized Customer Experiences
Personalization has become a cornerstone of effective marketing, and generative AI significantly enhances a brand’s ability to tailor content for individual users. By analyzing customer data — such as past purchases, browsing behavior, and demographic information — AI can generate personalized product recommendations, email subject lines, or landing page content that resonates with specific audience segments.
This level of customization can boost engagement and conversions, as users are more likely to respond to content that feels directly relevant to their interests.
Visual Content Generation
Beyond text, generative AI is being used to create visual assets. This includes everything from AI-generated product images to custom graphics and visual advertisements. Tools that generate images based on textual descriptions allow marketers to rapidly prototype visual concepts without needing a graphic designer for every iteration.
For instance, a brand launching a seasonal promotion might generate multiple image variations for testing, enabling data-driven decisions on which visuals perform best.
Social Media and Community Engagement
Social media marketers face the dual challenges of producing frequent content and engaging in real-time conversations. Generative AI assists by suggesting creative posts, responding to customer inquiries, and even composing replies that reflect the brand’s tone and guidelines. This helps maintain active engagement without requiring marketers to be online around the clock.
Email Marketing Optimization
Email remains one of the most effective channels for nurturing leads and driving conversions. Generative AI can enhance email marketing by creating tailored subject lines, generating segmented content variations, and even predicting optimal send times based on user behavior. Marketers can run tests and iterate rapidly, improving performance with less manual workload.
Product Descriptions and Catalog Management
E-commerce brands are finding value in using generative AI to automate product descriptions. Instead of manually crafting unique descriptions for hundreds or thousands of products, AI can generate engaging and SEO-friendly copy that highlights key features and benefits. This helps improve search visibility and provides a consistent brand voice across a product catalog.
Market Research and Trend Analysis
Generative AI models can analyze vast amounts of data — from social media conversations to industry reports — to help marketers identify emerging trends. This accelerates strategic decision-making, enabling teams to pivot quickly in response to market shifts.
For example, a brand may use AI tools to scan consumer sentiment around a new product category and adjust its product positioning based on insights gleaned from the analysis.
Benefits of Using Generative AI in Marketing
The adoption of generative AI in marketing brings several significant benefits. Understanding these advantages can help you evaluate whether and how to integrate these technologies into your workflow.
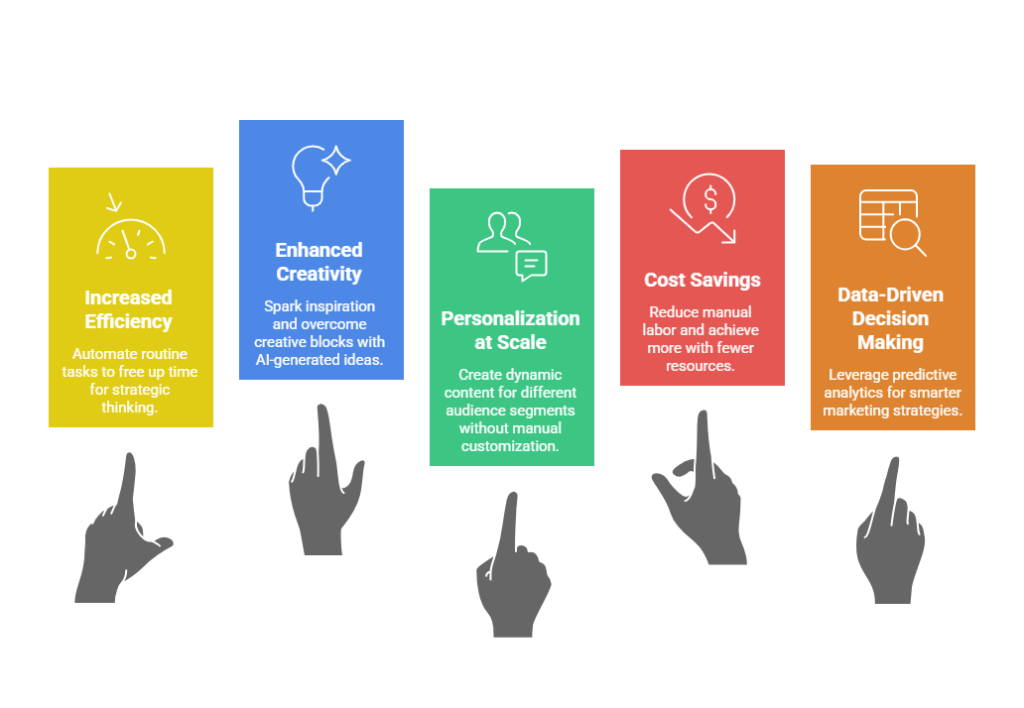
Increased Efficiency
One of the most direct benefits is efficiency. Routine tasks that once took hours can now be automated or completed much faster. This allows marketing teams to focus their time on strategic thinking, creative planning, and higher-level work.
Enhanced Creativity
Contrary to the fear that AI might stifle creativity, many marketers find that generative AI expands their creative possibilities. By providing multiple draft options, suggesting novel ideas, or generating unexpected combinations, these tools can spark inspiration and help human creators push past creative blocks.
Personalization at Scale
Personalized marketing has been a goal for many organizations, but executing it at scale has traditionally been difficult. Generative AI enables dynamic content creation that adapts to different audience segments without requiring manual customization for each individual.
Cost Savings
By improving productivity and reducing manual labor for repetitive tasks, generative AI can contribute to cost savings. Smaller teams, in particular, can achieve more with fewer resources, leveling the playing field with competitors that have larger marketing budgets.
Data-Driven Decision Making
Generative AI often incorporates predictive analytics and pattern recognition, allowing marketing teams to leverage data more effectively. Whether it’s identifying customer preferences or optimizing campaign performance, AI provides insights that can inform smarter decisions.
Challenges and Risks to Consider
Despite the many benefits, incorporating this advanced technology is not without challenges. Marketers need to be aware of potential pitfalls and take steps to mitigate them.
Quality Control
Generative AI outputs are only as good as the data they’re trained on. If the training data is biased, incomplete, or irrelevant, the content generated may be inaccurate, inappropriate, or off-brand. Rigorous review and editing are essential before publishing or deploying any AI-generated content.
Ethical Considerations
AI-generated content raises ethical questions about transparency and authenticity. Marketers must consider when and how to disclose the use of AI, particularly in communications where trust and credibility are paramount.
In addition, there’s the risk of producing misleading or harmful content if models are misused. Organizations should develop clear guidelines and guardrails for responsible AI use.
Data Privacy
Much of the power of generative systems comes from analyzing user data. Marketers must ensure compliance with data protection regulations such as GDPR and CCPA. Respecting customer privacy isn’t just a legal obligation — it’s essential for maintaining trust.
Dependence on Technology
Overreliance on automated systems can dull human skills. Marketers should use AI as a tool to enhance their work, not replace their expertise. Maintaining a balance between human judgment and machine output is critical for sustained success.
Best Practices for Implementing Generative AI
If you’re considering integrating generative AI into your marketing strategy, following best practices can help you get the most value while minimizing risks.
Start with a clear goal. Before deploying any generative tools, define what you want to achieve. Are you looking to speed up content creation? Improve personalization? Understand your objectives and select tools that align with those goals.
Invest in quality data. The effectiveness of generative models depends heavily on the data used to train them. Make sure your data is clean, relevant, and representative of the outcomes you want.
Establish review processes. Always include human oversight in your workflow. Editors and subject matter experts should review AI outputs for accuracy, tone, and alignment with brand standards.
Prioritize ethical use. Create guidelines for when and how AI can be used. Include considerations for transparency, user consent, and the avoidance of biased or misleading content.
Train your team. Equip your marketing team with the skills to use generative AI tools effectively. This may involve training workshops, tutorials, or hiring specialists who understand both the technology and marketing principles.
Measure performance. As with any marketing initiative, track the performance of AI-enhanced efforts. Use data to refine your approach, optimize workflows, and demonstrate ROI.
Tools and Platforms Powering Generative AI
There are many tools and platforms available today that make generative AI accessible to marketers, even those without technical expertise. These platforms range from text generators and image creators to full-scale marketing automation suites incorporating AI features.
Text generation tools can help produce blog content, social media posts, and email copy. Visual generators create customized imagery based on simple prompts. Other platforms integrate AI into customer relationship management, ad optimization, and customer segmentation, enabling seamless use of generated insights across channels.
As these technologies continue to evolve, the landscape of available tools is likely to expand, offering new capabilities and integration possibilities.
The Future of Marketing with AI
The convergence of artificial intelligence and marketing is more than a trend — it is a fundamental shift in how value is created and delivered to customers. As AI models become more advanced, we can expect even greater personalization, more sophisticated automation, and deeper integration between human creativity and machine intelligence.
In the coming years, generative systems may assist in real-time campaign adjustments, hyper-personalized content tailored to individual preferences, and intelligent customer interactions that feel truly conversational. Marketers who stay informed and adapt to these technologies will be better positioned to thrive in an increasingly competitive and dynamic landscape.
As you explore the possibilities, remember that generative AI in Marketing is not about replacing human ingenuity but amplifying it. The most successful strategies will combine the scale and speed of AI with the insight, empathy, and strategic thinking that humans bring to the table.

