Modern professionals rely heavily on digital platforms for recruiting, prospecting, research, and networking. Yet many users underestimate the power of advanced search techniques that can dramatically improve results. One of the most effective approaches involves combining Google’s Boolean logic with X-Ray searching to uncover public LinkedIn profile data that might otherwise remain hidden behind platform filters. This method allows recruiters, marketers, researchers, and sales specialists to locate specific individuals by role, skill, or organization with greater precision.
Boolean search itself is not a new concept. It refers to combining keywords with logical operators such as AND, OR, and NOT to produce more refined results. These operators allow users to include, exclude, or expand keywords in a query, making searches significantly more targeted and efficient. When applied through Google, Boolean operators work alongside special modifiers such as quotation marks or parentheses to structure complex search logic.
X-Ray search builds on this principle by applying those operators to specific domains like LinkedIn. It essentially instructs Google to look within LinkedIn’s publicly indexed pages and return only results that match defined criteria. The approach is widely used because Google’s indexing and query flexibility often produce more precise results than the native filters within the platform itself. This article explains how Google Boolean operators function, how they integrate with X-Ray methods, and how you can apply them effectively.
Understanding Boolean Logic in Search
What Boolean Operators Are and Why They Matter
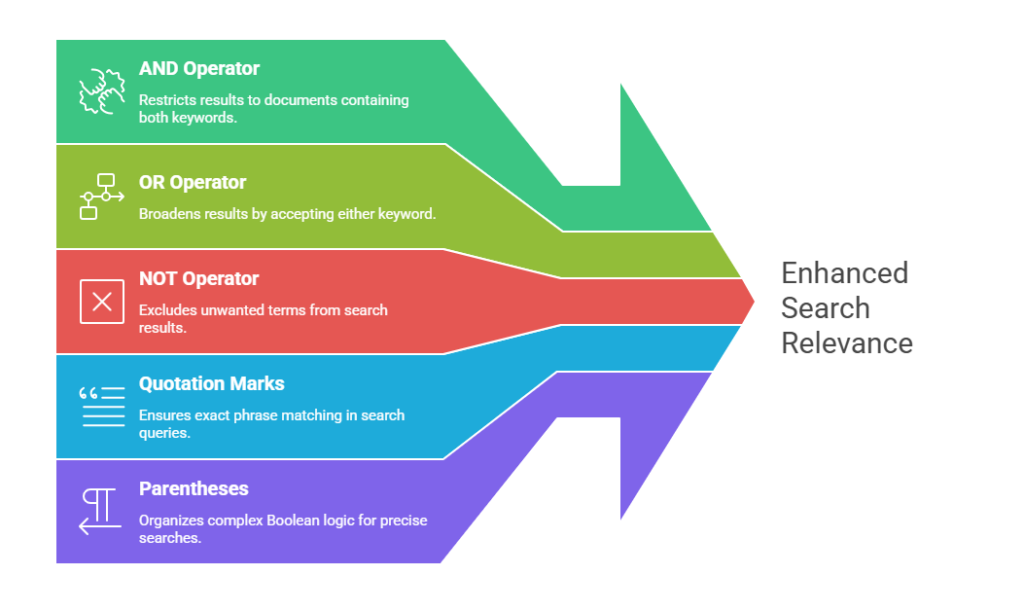
Boolean operators serve as connectors that help search engines interpret relationships between keywords. By combining words logically, they shape how search results are filtered or expanded. A simple Boolean query such as combining two keywords with AND restricts results to those containing both terms. Conversely, using OR broadens results by accepting either keyword, while NOT excludes unwanted terms.
Google supports these operators, although it already assumes an AND relationship between terms unless otherwise specified. In addition to standard operators, users can add quotation marks for exact phrases and parentheses to organize complex logic. These tools give searchers fine-grained control over relevance and specificity.
How Boolean Logic Applies to Professional Discovery
In recruitment or lead generation, search accuracy can directly influence productivity. For instance, a recruiter seeking professionals with particular technical expertise must avoid irrelevant matches while ensuring variations of job titles are included. Boolean logic allows them to express this need explicitly. Instead of manually reviewing thousands of profiles, they can structure queries that narrow results automatically. This capacity for precise targeting explains why Boolean search remains fundamental in sourcing workflows across industries.
Fundamentals of X-Ray Searching
Concept and Function
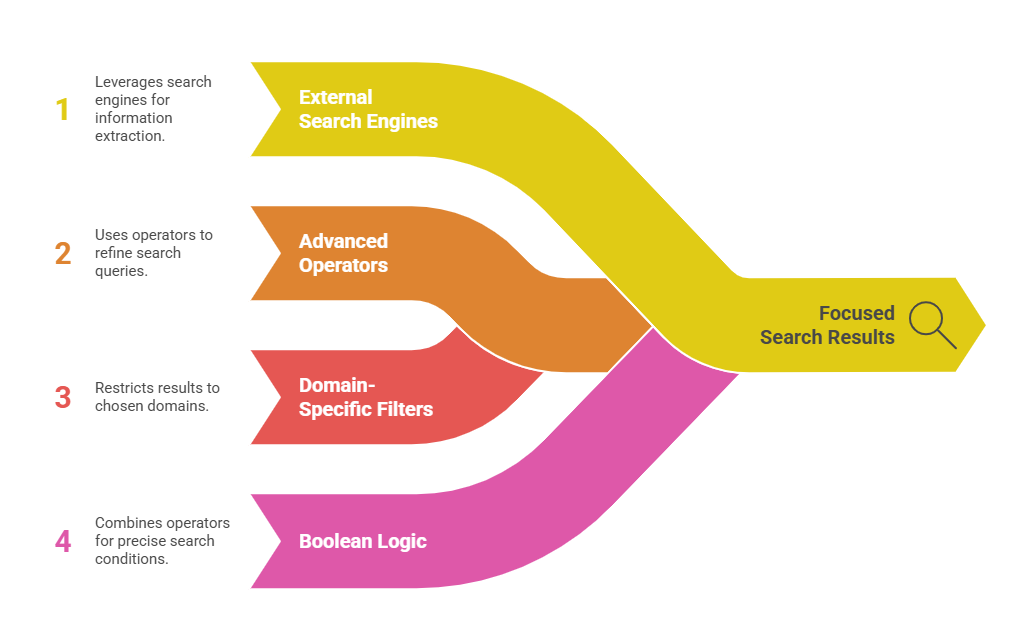
X-Ray search refers to the practice of leveraging external search engines to extract information from a specific website. It uses advanced operators to direct Google to retrieve results exclusively from chosen domains. This technique effectively turns the search engine into a focused discovery tool that scans public pages while ignoring unrelated content.
The approach is widely applied across social and professional networks because it improves access to publicly indexed data without requiring complex platform navigation. It can identify individuals by role, company, skill set, or geographic indicator while maintaining speed and efficiency. X-Ray search is frequently adopted by recruiters sourcing candidates, sales teams building prospect lists, or researchers seeking industry specialists.
Why Google Enhances LinkedIn Discovery
Google’s flexibility allows users to combine multiple Boolean operators with domain-specific filters like site: or inurl:. By entering a structured query that targets LinkedIn URLs, Google returns profile pages matching exact logical conditions. For example, using the site: operator restricts results to a particular domain, ensuring that only relevant LinkedIn pages appear. This combination of Boolean logic and domain restriction provides greater control over search outcomes.
linkedin xray search and the Role of Google Operators
Core Operators Explained
To use Google effectively for professional discovery, understanding the primary operators is essential. The site: modifier narrows results to LinkedIn pages by specifying the domain. AND ensures multiple conditions are satisfied simultaneously. OR enables inclusion of synonyms or alternate titles, while NOT removes unwanted keywords. Parentheses group complex logic sequences, quotation marks enforce exact phrase matching, and additional modifiers such as inurl: or intitle: refine placement of keywords within page structure.
These operators collectively create highly targeted queries. For instance, combining site restrictions with alternative job titles in parentheses ensures comprehensive coverage of terminology variations while still filtering by domain. Such structured logic significantly reduces noise in results and enhances search efficiency.
Example Query Construction
Consider the practical workflow of building a query. One begins by specifying the LinkedIn domain to restrict scope. Next, the exact job title might be enclosed in quotation marks to maintain phrase integrity. Additional keywords representing skills or tools are added with AND. Finally, unwanted categories or experience levels are removed with NOT or the minus symbol.
Google then returns indexed LinkedIn profile pages that match the complete logic sequence. Review and refinement follow, allowing adjustment of terms to improve relevance. Tools also exist that generate optimized Boolean strings automatically from natural-language inputs, demonstrating how adaptable and scalable this method has become.
Key Boolean Operators in Detail
AND Operator
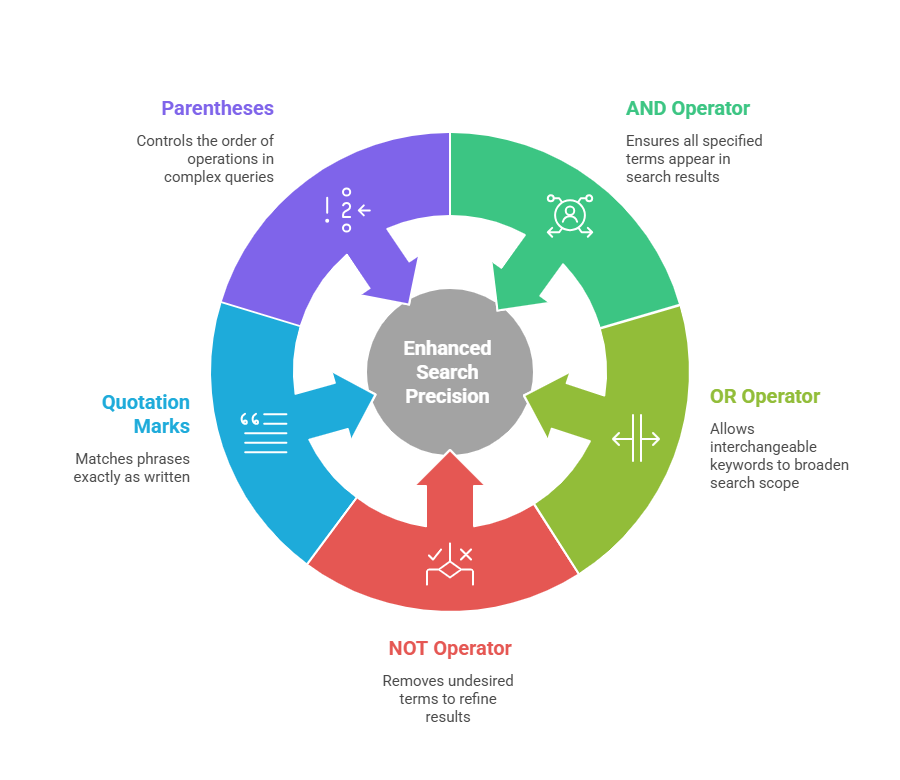
The AND operator joins multiple concepts, ensuring all specified terms appear in search results. Its purpose is to narrow results by enforcing keyword inclusion. This makes it especially valuable when searching for profiles requiring multiple competencies or attributes. When omitted in Google queries, AND is often implied automatically, yet explicitly using it clarifies intent in complex strings.
In sourcing contexts, AND allows precise combination of role, location, and technical skill, ensuring returned profiles align closely with defined criteria. Its value lies in eliminating partial matches that could otherwise dilute search accuracy.
OR Operator
OR broadens search scope by allowing interchangeable keywords. Because different organizations may describe identical roles using varying terminology, OR ensures coverage of synonyms and variations. Using this operator significantly expands the search horizon without compromising logical structure.
In professional discovery, OR is frequently applied when accounting for job title diversity or alternative skill naming conventions. It helps capture the full spectrum of relevant results that might otherwise remain fragmented across inconsistent language usage.
NOT Operator and Exclusion Techniques
The NOT operator removes undesired terms, allowing users to refine results further. Google also supports the minus symbol as an equivalent exclusion tool. This capability is essential when filtering out irrelevant roles, junior experience levels, or unrelated industries that might appear due to keyword overlap.
Exclusion ensures searches remain aligned with specific objectives. By systematically removing unwanted categories, users maintain precision while still exploring large datasets.
Quotation Marks and Exact Matching
Quotation marks instruct search engines to match phrases exactly as written. Without them, engines may treat words independently and return broader results. Exact matching is critical when searching for standardized job titles or specialized terminology.
The precision of phrase matching reduces ambiguity and strengthens search reliability. It ensures that results reflect true semantic alignment rather than loose keyword coincidence.
Parentheses and Logical Grouping
Parentheses control the order of operations in complex queries. They group keywords and operators to define logical relationships clearly. Without parentheses, search engines may interpret sequences differently, resulting in unintended outputs.
Logical grouping is particularly useful when combining multiple OR conditions with AND constraints. It ensures that expanded keyword sets remain connected to core search requirements.
Practical Implementation Workflow
Planning the Search Strategy
Effective search begins with identifying target attributes. These might include job title variations, required competencies, industry keywords, and geographic identifiers. Mapping these factors ensures logical structure before constructing queries.
The next step involves organizing keywords into inclusion, expansion, and exclusion categories. This preparation simplifies operator selection and prevents overly complicated strings that could produce inconsistent results.
Executing and Refining Queries
After constructing the initial query, execution through Google yields a list of LinkedIn pages matching conditions. Reviewing these results provides insights into effectiveness. Adjustments may involve adding synonyms, tightening phrase matches, or removing unnecessary exclusions.
Continuous refinement is central to mastering this process. Over time, users develop intuition regarding optimal operator placement and keyword combinations.
Evaluating Results for Accuracy
Interpreting returned profiles requires careful review. While Boolean logic improves targeting, contextual verification ensures individuals genuinely meet criteria. Iterative adjustments based on evaluation lead to progressively higher-quality outcomes.
This process underscores that Boolean searching is both analytical and adaptive, blending logical structuring with human judgment.
Limitations and Considerations
Platform Constraints
Although Boolean searching offers extensive flexibility, platform indexing and filtering limitations may affect outcomes. Not all LinkedIn search fields support Boolean logic equally, and certain filters like location or industry may not integrate directly within native platform searching. External search engines compensate for these constraints by providing broader control over logic structure.
Ethical and Practical Usage
X-Ray searching operates exclusively on publicly accessible data. It does not bypass privacy controls or access restricted information. Its effectiveness stems from intelligent query design rather than unauthorized data retrieval. Users should employ these techniques responsibly and transparently within professional contexts.
Strategic Advantages
Efficiency Gains
Structured Boolean queries reduce manual screening time by automating filtering logic. They enable professionals to move quickly from broad exploration to targeted discovery. This efficiency is particularly valuable in high-volume sourcing environments where speed and relevance are critical.
Enhanced Precision
Precision emerges from logical consistency. By explicitly defining relationships between keywords, users eliminate guesswork and achieve predictable outcomes. This level of control supports reliable workflow integration across recruitment, sales, and research functions.
Scalability Across Use Cases
The adaptability of Boolean logic allows application across industries and objectives. Whether identifying talent pools, mapping competitive landscapes, or researching sector experts, structured queries maintain relevance across diverse scenarios.
Conclusion
Google Boolean operators provide a powerful framework for structured information retrieval. When combined with X-Ray methodology, they transform general web searching into a focused professional discovery mechanism capable of delivering highly targeted results. By mastering logical connectors, modifiers, and grouping techniques, users gain substantial control over relevance and precision.
The method’s effectiveness lies in its blend of simplicity and depth. Operators such as AND, OR, and NOT form the foundation, while quotation marks and parentheses add nuance. Domain restrictions guide search scope, enabling professionals to uncover profiles aligned with defined objectives.
Mastering linkedin xray search techniques requires practice, experimentation, and continuous refinement, yet the rewards include enhanced efficiency, accuracy, and scalability in professional information gathering. With a disciplined approach to Boolean logic, users can leverage search engines not merely as lookup tools but as strategic discovery platforms capable of unlocking valuable insights across the digital professional landscape.

